EXPERIENCE REALISM, ENHANCE RESILIENCE
AND INCREASE EFFICIENCY
The decision-making of professional rescuers is influenced by high levels of perceived stress. Training with simulations of real-stress situations significantly enhances their ability to perform effective CPR, reinforcing standard procedures when additional devices such as defibrillators or pulmonary ventilators are required.
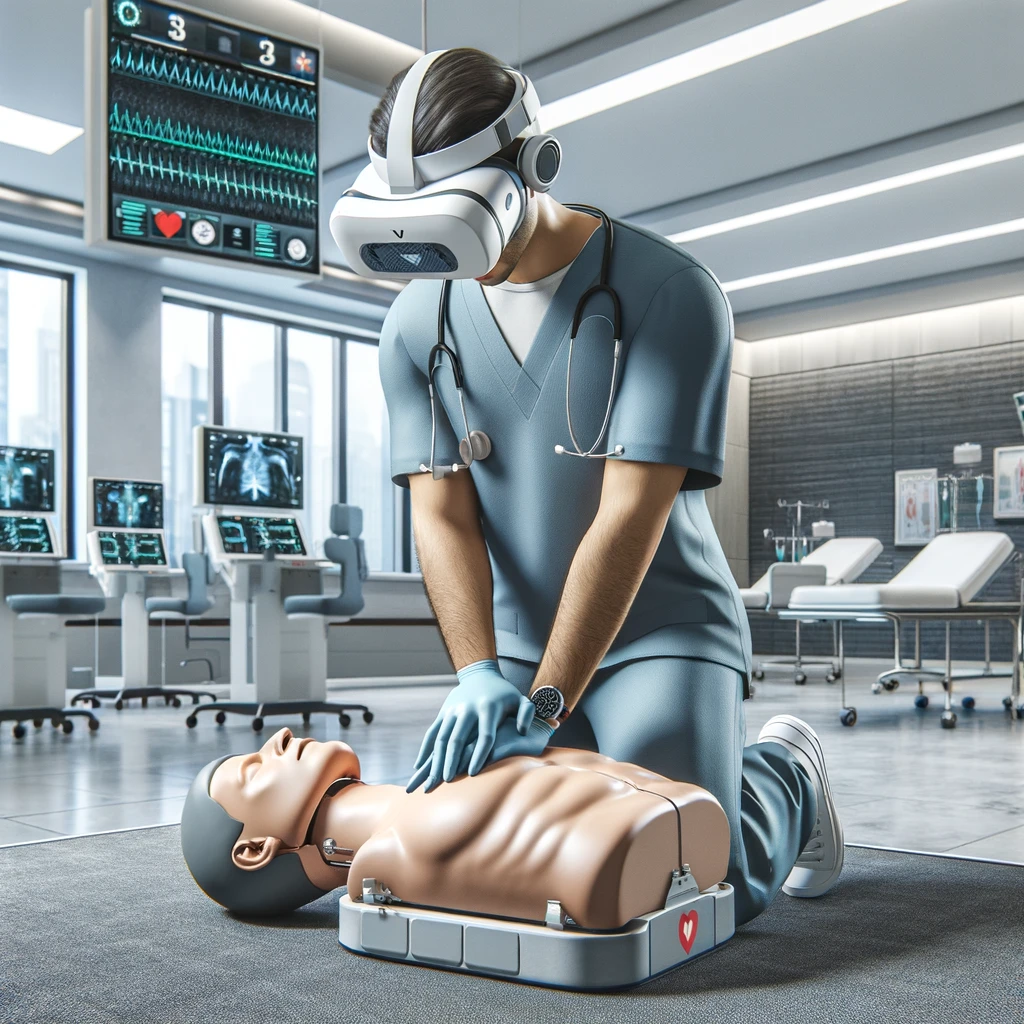
ADVANTAGES OF VR CPR

- Cutting-edge VR technology immerses participants in lifelike emergency scenarios, offering training in a risk-free environment.
- Immersion in meticulously crafted crisis scenarios that mirror real emergencies, featuring chaotic settings and unexpected challenges hones decision-making skills under pressure.
- Immediate, precise feedback is received through integrated sensors, providing real-time insights into training progress and skill development.
- The opportunity to make crucial errors within a controlled virtual environment allows for learning from these experiences to pinpoint specific triggers leading to mistakes, recognize risky habits, and improve skills.
- Practicing in high-stress environments cultivates the composure and focus necessary for critical moments.
TRUSTED PARTNERS
Who is VR CPR PRO designed for?

Versatile training is designed for units whose mission is to save lives
in sudden cardiac arrest and critical comorbidities:
- Paramedics
- Firefighters
- Police
- Military
- Mountain rescue
- Hospitals and more

TRAINING APPLICATION FEATURES
- Connecting dummies to the virtual accident scene
- Realistic sounds, lifelike visual cues
- Creating genuine, high-stress simulations
- Authentic patient responses
- Instant feedback and training assessment
- Training for additional devices such as a defibrillator, pulmonary ventilator, etc.
- Distinct environments
- Adherence to ERC standards
PROVEN RESULTS
4x
V-learners can be trained 4 times faster than in traditional classrooms
275 %
more confident in applying skills learned after training
96 %
of V-learners want to continue with VR training
STAY UP TO DATE WITH VR / AR / AI TRENDS
CONTACT US
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTION
VR apps can detect manikins and link haptics to the visual experience within the app. The VR CPR app can be used for all types of manikins produced.
The app offers realistic sounds and visual cues to create an authentic training environment and help users respond effectively to to crises.
Scenarios are created based on practice requirements and in collaboration with experts. The request for VR training came from the German ASB rescue service. An international advisory board oversees the development of scenarios and procedures. A prototype of the VR CPR app has been tested by medical staff in several countries and the app is continuously modified and expanded according to their feedback.
VR training creates simulations of real situations and allows learning through experience. Learning from experience trains skills, the principle of learning is different, knowledge/skill retention is longer and learning is more effective. The ability to learn from mistakes and work under stress is important. VR CPR reinforces good practice and increases confidence in applying newly learned skills in real life.
VR CPR comes in two versions: VR CPR Public for the general public and VR CPR PRO for professionals. Each version has multiple environments and modes. The environments are selected based on the needs of the target audience. The PRO version also focuses on the use of other devices such as a defibrillator or pulmonary ventilator. The public version, on the other hand, focuses on good practices for laypeople, including the availability of AEDs on the street or in public buildings.
Yes, the scenarios are designed by the ERC standards to improve the skills of paramedics in providing care to patients in critical situations, including cardiac arrests and other conditions requiring immediate resuscitation.
The workouts are set up in minutes. The CPR training takes a maximum of around 10 minutes. The evaluation of the training takes place with the trainer outside of the virtual environment. Then you can take another round. In addition, the latest versions of VR headsets along with the computer-generated environment minimize the risk of motion sickness that used to be with other technologies e.g. 360 videos. The VR CPR app is also user-tested for safety and comfort of use.
PARTNERS
- Malteser
- Záchranka
- Med Muni
- Charité
- ASB
- Nadace Vodafone
- Bayern Labs
- XR HUB BAVARIA
CONTACT
- Leoš Kubíček
- leos@virtual-lab.cz
- +420 724 250 603
- VIRTUAL LAB, S.R.O.
- Company number: 08065811
- Lipová 1789/9
- 370 05 České Budějovice 2

